|
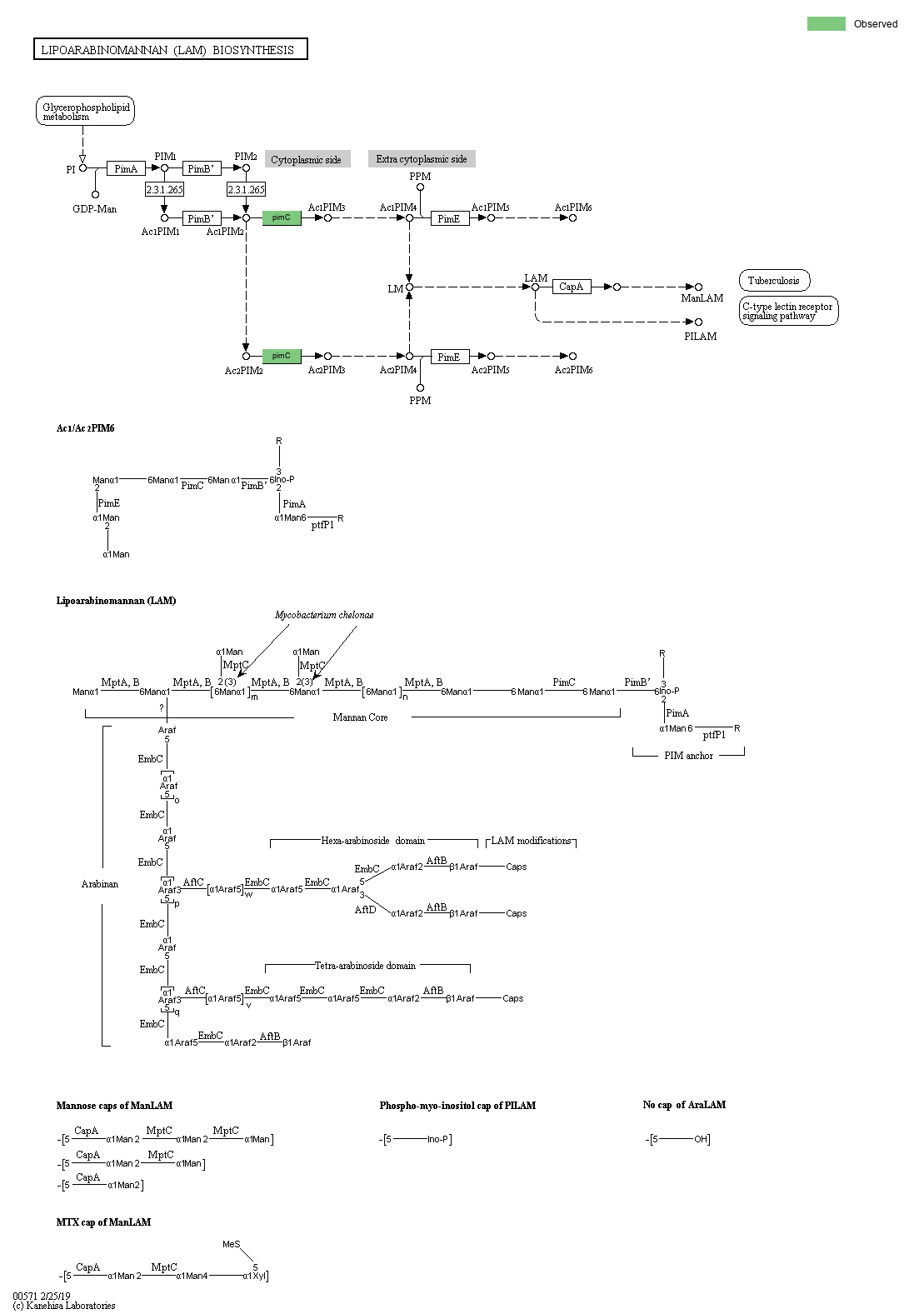
Lipoarabinomannan (LAM), as well as structurally related lipomannan (LM) and phosphatidylinositol mannosides (PIMs), are major glycolipids found on the mycobacterial cell wall. LAM is synthesized from phosphatidylinositol (PI) and in a biochemical pathway of PI => PIMs => LM =>LAM. Structually, LAM and LM are an extension of PIMs containing an alpha1,6-linked mannan core with alpha1,2-monomannose side chains. The mannan core of LAM is in turn arabinosylated by a linear alpha1,5-linked Araf backbone, punctutated by alpha1,3-linked branching. LAM can be substituted by several capping motifs, which determine the ability of LAM to modulate the immune response through the interaction with different receptors containing C-type lectins (
map04625
). It has been shown that the immunomodulatory properties of LAM and related glycolipids contribute to the survival of Mycobacteriaum tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis (
map05152
).
|
 Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) biosynthesis - Reference pathway
Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) biosynthesis - Reference pathway

 Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) biosynthesis - Reference pathway
Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) biosynthesis - Reference pathway